July 7, 2025
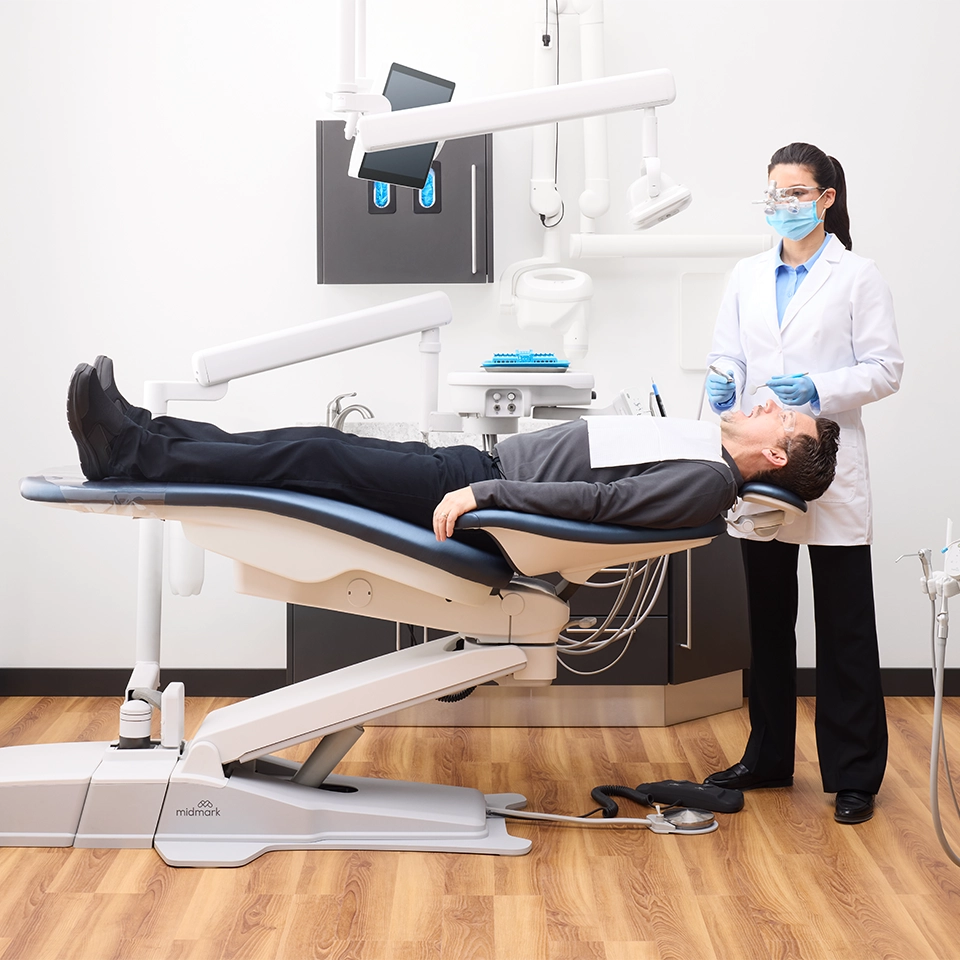
Proper dental equipment sterilization—specifically, the sterilization of reusable instruments like handpieces, scalers and mirrors—is a cornerstone of professional dental care. Instrument processing using specialized equipment like autoclaves, ultrasonic cleaners and supporting clinical cabinetry is critical to ensuring these tools are thoroughly decontaminated between uses. Though vital to patient safety and trust, it’s not always appreciated that this process involves a series of meticulous steps, each requiring careful attention to detail.
This article aims to guide dental professionals through the best practices for sterilizing dental instruments. It's designed to provide insights into effective infection control measures and sterilization protocols. We'll explore the types of dental sterilization machines, their uses, and the step-by-step process of cleaning and sterilizing dental instruments. We'll discuss the importance of personal protective equipment (PPE) and how to monitor sterilization effectiveness. We'll also explain how to optimize your dental practice design and workflow for safety and efficiency. Lastly, we'll touch on the importance of educating your team and patients about these protocols.
By the end of this article, you'll have a deeper understanding of dental equipment sterilization, empowering you to enhance your practice's safety measures and patient satisfaction.
Understanding the Importance of Dental Instrument Sterilization Protocols
Dental instruments frequently come into contact with saliva, blood and other biological materials. These interactions heighten the risk of pathogen transmission, including bacteria, viruses and fungi.
Among the pathogens that can lurk on dental instruments are harmful bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus species. Viruses such as hepatitis B, hepatitis C and HIV are potential threats without proper sterilization protocols in place.
Potential Concerning Pathogens on Dental Instruments:
- Bacteria: Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus species
- Viruses: hepatitis B, hepatitis C, HIV
- Fungi: Candida species
The significance of instrument processing extends beyond mere procedure. It's a crucial factor in safeguarding patient and teammate health and preventing cross-contamination. Effective sterilization diminishes infection risk, ensuring a safe environment for dental care.
Moreover, consistent and thorough sterilization practices elevate patient trust. Patients expect a clean, safe space for their dental treatments. When they perceive strict adherence to sterilization protocols, confidence in the practice soars.
Emphasizing sterilization not only maintains compliance with healthcare standards but also fosters a culture of safety and professionalism. This emphasis enhances the overall patient experience, contributing to patient loyalty and positive word-of-mouth referrals. Recognizing the impact of thorough sterilization is key to running a successful dental practice.
Implementing Effective Sterilization Solutions
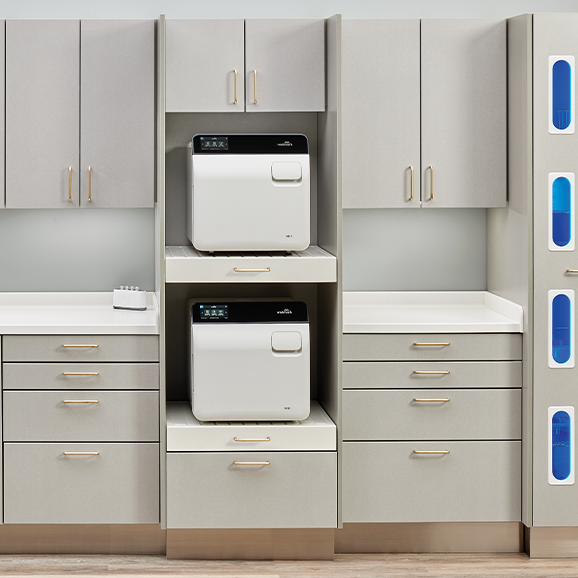
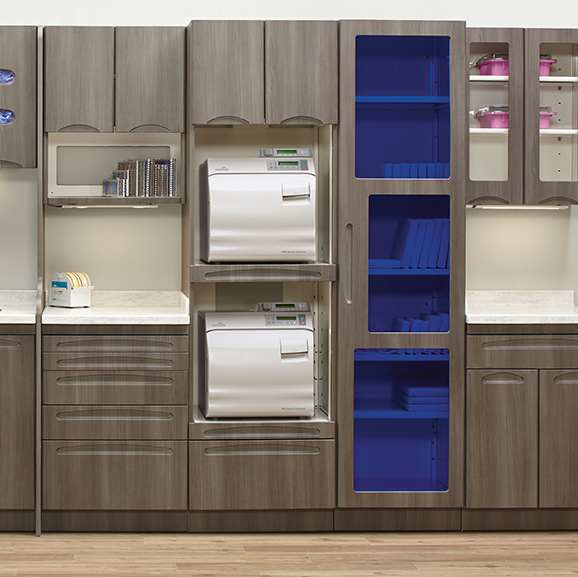
Modern dental practices require comprehensive sterilization systems that ensure both safety and efficiency. For example, Midmark Synthesis® and Artizan® Expressions Sterilization Center Cabinetry collections provide a carefully designed workflow that follows the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommended dirty-to-clean process. The cabinetry’s ergonomic design includes:
- Dedicated zones that follow the CDC practice of dirty to clean
- Seamless, clinical-grade surfaces that resist moisture and bacteria
- Built-in organization systems that streamline the sterilization process
When setting up your sterilization area, consider implementing a layout that accommodates your practice's specific needs and available space. The design should follow a standardized 5-step instrument processing workflow for better adherence to clinical best practices. You have several efficient configuration options:
- U-shaped design: Ideal for large practices that demand multiple sterilizers. This layout provides ample surface areas and a one-way flow that allow more team members to multitask simultaneously and maintain a bustling workflow.
- Galley design: Features workspaces on two opposing walls with a single traffic lane between them. This arrangement allows for easy access and efficient workflow, helping your team maintain momentum using a linear flow while keeping everything within reach.
- L-shaped design: Maximizes use of available space where elbow room is limited. This configuration proves that the space you have can be all you need to process instruments effectively and safely.
- Straight-line design: Perfectly suited to the 5-step instrument processing workflow, this layout can help maximize efficiency for effective infection prevention in a narrow space.
For optimal efficiency, the sterilization area should be centrally located—ideally no farther than three operatories away from any treatment room. See the Midmark Instrument Processing Brochure for more information.
Choosing the Right Equipment
Selection of proper sterilization equipment is crucial for maintaining effective infection control. Key considerations include:
- Sterilization Technology: Modern autoclaves for dental instruments like the Midmark M11® and M9® Steam Sterilizers provide reliable sterilization while offering features such as an intuitive user interface with built-in prompts and more unique preset and custom cycles than most sterilizers.
- Cabinetry and Surfaces: Opt for clinical-grade solutions like Midmark Synthesis cabinetry with seamless polystyrene drawers, heat and moisture-resistant surfaces, and easy-to-clean, bactericidal cabinet and drawer handles.
- Equipment Capacity: Match sterilizers and ultrasonic cleaners to your practice size. Consider the following recommendations for typical practice sizes:
- 1-2 Doctors and 2-4 Hygienists: 2 sterilizers (either 2 M11® or 1 M11 and 1 M9®) with a QuickClean® QC3 ultrasonic cleaner
- 3 Doctors and 3-5 Hygienists: 3 sterilizers (either 3 M11 or 2 M11 and 1 M9) with a QuickClean QC6 ultrasonic cleaner
- 4 Doctors and 4-6 Hygienists: 4 sterilizers (either 4 M11 or 3 M11 and 1 M9) with a QuickClean QC6 ultrasonic cleaner
Insufficient equipment capacity can slow down your practice and increase labor costs, making proper sizing essential for efficient workflow.
Also consider:
- Processing Practices:
- Cassettes vs. Pouches: If you use cassettes, which help process more instruments than pouches in one load, you'll need larger sterilizers (chamber of at least 11 inches) and ultrasonic cleaners (at least 3 gallons).
- Handpiece Maintenance: Consider adding a dedicated handpiece cleaning device like the Lubricare 2® Handpiece Care and Maintenance System for consistent, repeatable results.
- Monitoring Capabilities: Choose sterilizers that automatically capture routine care events and cycle information to ensure proper documentation.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluate long-term operating costs, not just the initial purchase price. Midmark M9® and M11® sterilizers require no additional air or water filtration accessories, no expensive daily vacuum tests and only infrequent technician service. Combined with a longer product life of 10 years or 25,000 cycles, these advantages can help your office save thousands compared to competitive models.
- Workflow Integration: Consider how your sterilization center connects to treatment areas. Midmark design experts recommend planning around 120 square feet per operatory to accommodate proper workflow and safety protocols. For maximum efficiency, ensure your sterilization center is centrally located, with the farthest operatory no more than three operatories away.
CDC Guidelines and Types of Dental Sterilization Machines
The CDC sets crucial guidelines for infection control in dental settings. These guidelines provide essential protocols to mitigate infection risks, ensuring patient and staff safety. Adhering to CDC protocols helps maintain high standards in dental sterilization practices.
Following CDC guidelines along with defined local, state and federal guidelines is not merely a best practice but a fundamental part of regulatory compliance. These guidelines include recommendations on hand hygiene, the use of personal protective equipment and environmental infection control. Compliance with these guidelines helps dental practices avoid legal issues and ensures comprehensive infection control.
In dental sterilization, the choice of equipment matters greatly. Various machines serve different purposes, and their correct application enhances sterilization efficacy.
Types of Dental Sterilization Machines
- Steam Sterilizers: Use steam and pressure to eliminate microbial life, including spores. Ideal for most dental instruments.
- Chemical Vapor Sterilizers: Utilize hot chemical vapors to sterilize equipment. Suitable for instruments sensitive to moisture.
- Dry Heat Sterilizers: Apply high temperatures without moisture, appropriate for materials that might corrode with steam.
Modern Autoclave Advantages
Modern autoclaves enhance traditional sterilization methods with significant improvements. The Midmark M9 and M11 offer several advantages in three critical areas:
- Durability
- Extended lifespan: Designed for an impressive 25,000-cycle life thanks to a completely re-engineered chamber
- Reduced maintenance: Cuts required maintenance frequency by users and certified technicians by more than half
- Long-term reliability: Robust construction helps ensure consistent performance through years of daily use
- Workflow Efficiency
- Intuitive user interface: Uses a 5-inch touchscreen with clear, graphical display that is operable even when wearing gloves
- Visual status indicators: Employs a color-coded LED light bar and countdown clock that are visible from across the room
- Multilingual capability: Provides English, French or Spanish for your preferred display language
- Optimized instrument processing: Supports CDC and AAMI-recommended dirty-to-clean workflow to contain contamination and maximize efficiency
- Compliance Assurance
- Automated documentation: Maintains comprehensive mechanical monitoring and chemical indicator reporting
- User authentication: Tracks operator activity for better accountability
- Unlimited storage: Retains routine care events for the entire life of the sterilizer
- Automatic notifications: Delivers timely reminders for required care
- Audit-ready records: Simplifies compliance with device reminders, notifications and automated cycle recordkeeping
These advancements in sterilization technology not only ensure thorough instrument processing but also contribute to more efficient practice operations, reduced teammate stress and maintained regulatory compliance. The M11 autoclave represents a significant step forward in dental sterilization, providing comprehensive benefits that extend well beyond basic instrument sterilization.
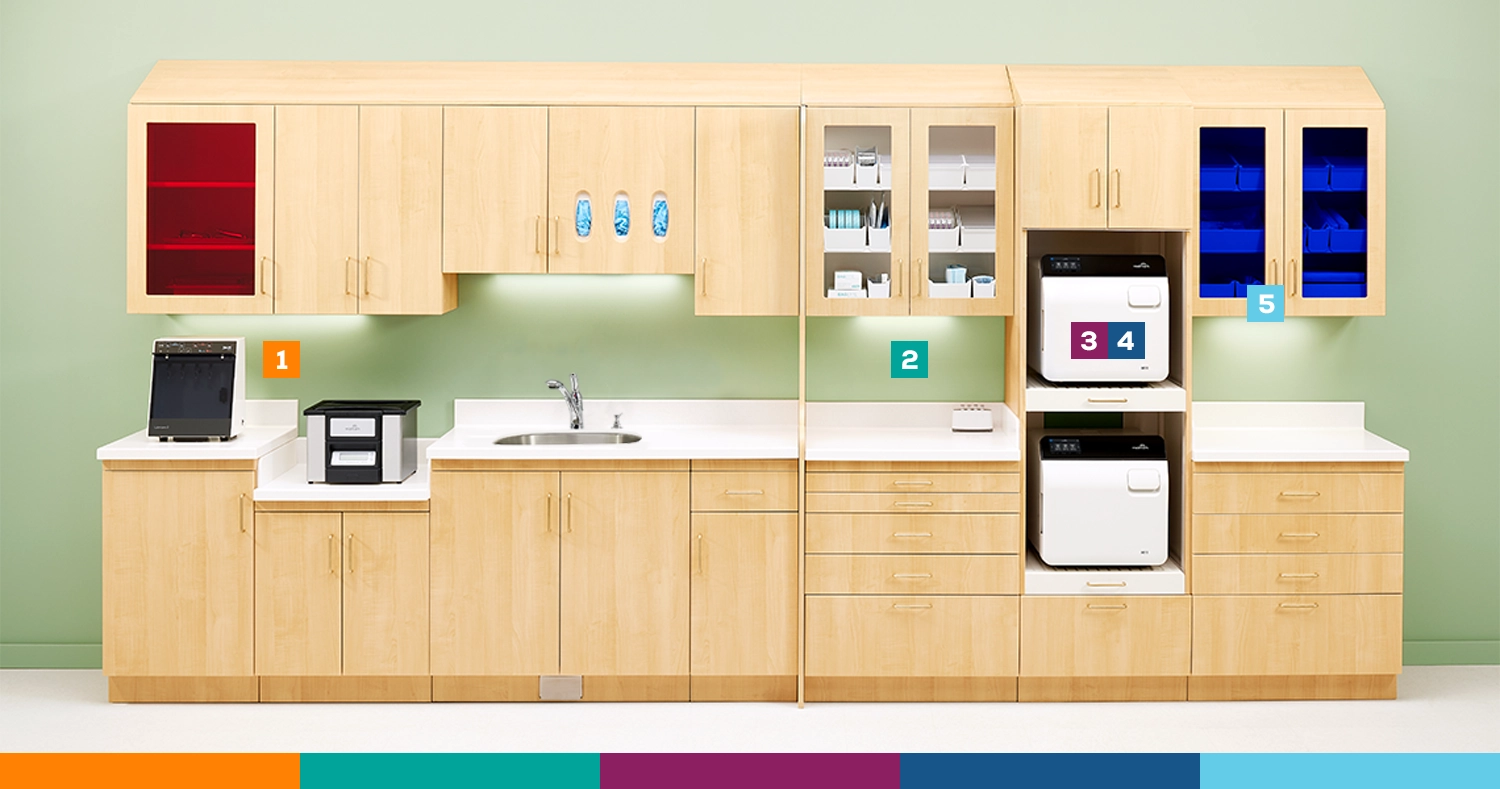
5-Step Instrument Processing Workflow
Following a dirty-to-clean instrument processing workflow as recommended by the CDC and AAMI helps contain contamination and maximize the efficiency of your instrument cleaning and sterilizing process. Here's a standardized 5-step approach to ensure proper infection control:
Step 1: Receiving + Cleaning
Reusable instruments, supplies and equipment should be received, cleaned and decontaminated in one section of the processing environment. Remember to clean handpieces on both the outside and inside. This initial step removes visible debris and prepares instruments for sterilization. Follow the manufacturer instructions for use (IFU) on cleaning each instrument.
Step 2: Preparation + Packaging
Cleaned, dried instruments and other supplies should be inspected for residual debris and damage, assembled into sets or trays, and wrapped or packaged for sterilization. Proper packaging maintains sterility after processing and allows for organized storage.
Step 3: Sterilization
The sterilization area should include the sterilizer and related supplies with adequate space for loading and unloading the sterilizer. Follow the manufacturer IFU carefully to sterilize dental instruments effectively and consistently. This step ensures complete eradication of all microbial life.
Step 4: Monitoring/Sterility Assurance
Mechanical, chemical and biological monitoring should be used to ensure the efficacy of the sterilization process. Results of sterilization need to be recorded. This critical verification step confirms that sterilization parameters were met during each cycle.
Step 5: Storage
The storage area should be adequately sized, closed or covered, and located apart from contaminated instruments in an area protected from moisture. Supplies and instruments should not be stored under the sink. Proper storage maintains sterility until use.
By following these guidelines, implementing an effective process and using the right dental sterilization machine, your team can confidently sterilize dental instruments and uphold the highest infection control standards.
Implementing an Effective Process
Implementing this 5-step workflow minimizes the risk of cross-contamination and infection effectively. It is also essential to ensure proper training for all staff involved in the sterilization process.
Each area of your sterilization center should be clearly designated for its specific purpose in the workflow, with visual cues that help staff maintain the proper directional flow from dirty to clean. This separation is fundamental to preventing cross-contamination.
Understanding and executing each step with diligence enhances patient trust and safety in your dental practice. Regular reviews of these protocols further strengthen your team's ability to maintain high instrument processing standards.
By following the CDC and AAMI recommendations for reprocessing, dental practices can ensure a systematic approach to infection prevention that protects both patients and staff while maximizing operational efficiency.
Creating an Optimized Sterilization Environment
When designing your sterilization area, select cabinetry engineered to support proper workflow and safety protocols. The Synthesis® Sterilization Center implements the CDC-recommended dirty-to-clean workflow through:
- Clear zone designation for:
- Receiving and cleaning
- Preparation and packaging
- Sterilization
- Monitoring/Sterility assurance
- Clean storage
- Integrated workflow features such as:
- Heavy-duty pull-out shelves that support and provide access to the sterilizer
- Hands-free waste management solutions
- Anti-microbial cabinet handles
- Aseptic, non-porous counter materials like solid surface and quartz
Best Practices for Handling and Transporting Contaminated Instruments
Safe handling of contaminated instruments is crucial to prevent cross-contamination and potential injury. Establishing clear protocols for the safe handling of contaminated instruments ensures that all team members understand and consistently follow the necessary precautions. It also maintains the integrity of infection control measures throughout the practice.
Dental team members should transport contaminated instruments from operatories to instrument processing areas using methods that minimize exposure risk and prevent cross-contamination. Best practices and guidelines recommend these practices:
- Minimize Handling: Handling of loose contaminated instruments should be minimized during transport.
- Use Covered Containers: Instruments should be carried in a covered container to reduce the potential for exposure to blood or other potentially infectious materials.
- Implement Work-Practice Controls: Work-practice controls, such as using containers specifically designed for safe transport, help to further minimize exposure potential.
Teammates should wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling contaminated instruments. Gloves, masks, gowns and protective eyewear shield team members from potential exposures. While PPE is not typically required for transport once instruments are placed in covered containers, training the team on safe handling procedures and the importance of PPE in appropriate zones can significantly enhance overall safety.
Training Teammates on the Safe Handling of Contaminated Instruments
Regular training sessions should emphasize the safe handling of contaminated instruments, including how to properly use covered transport containers, wear appropriate PPE and follow designated workflows. This emphasis not only enhances infection control but also promotes a culture of safety and accountability in the dental practice.
Furthermore, regular audits of handling practices can identify areas for improvement. Encourage team feedback to refine and strengthen these protocols. By prioritizing safe transportation and handling practices, your dental practice can maintain a high standard of patient care and safety.
Optimizing Storage and Transport Solutions
The Midmark Synthesis® cabinetry collection supports safety through:
- Color-coded storage areas that clearly differentiate clean and contaminated items
- Seamless construction that prevents bacterial growth
- Moisture-resistant materials ideal for sterilization areas
- Mobile storage options for efficient transport
PPE and Monitoring Sterilization Effectiveness
The use of personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential during the decontamination process to protect staff. PPE such as gloves, masks, gowns and protective eyewear shields workers from harmful microorganisms. These barriers are vital when handling contaminated instruments during cleaning and disinfection.
According to the Basic Expectations for Safe Care outlined by the CDC, dental practices should routinely verify sterilization effectiveness using a combination of biological, mechanical and chemical indicators.
Biological indicators, commonly known as spore tests, are considered the most definitive method because they assess whether highly resistant microorganisms (e.g., Geobacillus or Bacillus species) have been destroyed. These tests should be performed at least weekly, though results are not immediate. Because results are delayed, mechanical and chemical indicators are used more frequently to provide real-time feedback and help identify procedural errors or equipment malfunctions.
Mechanical indicators monitor sterilizer performance by displaying key parameters—such as pressure, temperature and exposure time—on readouts or printouts. These should be reviewed during each cycle and documented for recordkeeping.
Chemical indicators provide more immediate feedback. They change color when exposed to appropriate sterilization conditions and are used both inside and outside instrument packages. A failed indicator result means instruments must not be used, helping to prevent the accidental use of non-sterile items.
Maintaining thorough sterilization records and routinely inspecting packaging for signs of compromise (e.g., tears, moisture) are essential steps in ensuring both patient safety and procedural accountability.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Sterilization Equipment
Proper maintenance of dental sterilization machines is crucial for their efficient operation. Regular servicing helps prevent unexpected breakdowns, supports consistent performance and prolongs the lifespan of the equipment. Routine checks and timely part replacements help ensure machines function at their optimal levels. Just as important, keeping detailed maintenance records is a critical part of a dental infection prevention program. These records confirm that service has been properly completed, support accountability and provide documentation if an issue ever needs to be traced.
Troubleshooting tips can also help resolve minor equipment issues quickly with minimal downtime. Keeping a log of machine performance and maintenance activities aids in identifying recurring problems. When issues arise, refer to the manufacturer's manual or consult a qualified technician for guidance. By prioritizing routine maintenance and swift troubleshooting, dental practices can maintain smooth operations and uphold high sterilization standards.
Equipment Maintenance Best Practices
For optimal performance of your Midmark sterilization equipment:
- Use only manufacturer-recommended cleaning solutions
- Maintain proper water quality for steam sterilizers
- Keep detailed maintenance logs for compliance
Contact Midmark Technical Service at 1.844.856.1231 for product support or technician scheduling.
Designing an Efficient Sterilization Workflow in Your Dental Practice
The design of a dental practice significantly influences infection control measures and overall workflow. Research shows dental teams may access the sterilization area 80-120 times daily, making an optimal layout crucial. Midmark Synthesis® Sterilization Center Cabinetry offers four proven configurations:
- Straight-line Layout:
- Ideal for maximizing efficiency in instrument processing
- Perfect for implementing the CDC-recommended dirty-to-clean workflow
- Requires minimum of 10-12 feet of linear space for single-doctor practices
- Galley-style Layout:
- Optimal for practices with multiple teammates working simultaneously
- Features workspaces on opposing walls
- Keeps all essentials within easy reach
- L-shaped Design:
- Maximizes corner spaces effectively
- Maintains proper workflow in smaller areas
- Ideal for compact sterilization centers
- U-shaped Layout:
- Perfect for larger practices
- Provides ample surface areas for multiple team members
- Offers maximum storage capacity
Each configuration incorporates clinical-grade design features like:
- Seamless, moisture-resistant surfaces
- Integrated organization systems
- Aseptic, non-porous counter materials
- Hands-free features for infection control
Consider the following tips for creating an efficient sterilization workflow:
- Dedicated Zones: Establish clear zones for receiving and cleaning, preparing and packaging, sterilizing, monitoring/assuring sterility, and storing instruments to streamline processes.
- Ergonomic Design: Position equipment ergonomically to reduce strain on staff and improve process speed.
- Storage Solutions: Utilize storage systems to organize instruments, reducing the time spent searching for needed items.
Enhanced Storage Solutions
Midmark Synthesis® cabinetry provides:
- Seamless polystyrene drawers that prevent contamination
- Heat and moisture-resistant surfaces
- Bactericidal cabinet handles
- Integrated workflow design features
Implementing a systematic workflow not only boosts staff efficiency but also builds patient confidence in your practice. When patients see a well-structured environment, they perceive the practice as professional and trustworthy. Ultimately, an effective workflow ensures that dental practices meet high standards of safety and quality, benefiting both staff and patients.
Educating Your Team and Patients About Sterilization Protocols
Team Training and Development
Maintaining high safety standards begins with comprehensive staff education on sterilization protocols. Engage your team through:
- Regular training sessions on the latest sterilization practices
- Hands-on workshops for practical skill development
- Continuous learning modules to reinforce knowledge
- Monthly updates on new protocols and equipment procedures
Patient Communication Strategies
Help patients understand your commitment to their safety through effective communication:
- Use clear, non-technical language to explain sterilization procedures
- Display educational materials in waiting areas
- Share sterilization protocols during patient consultations
- Highlight your practice's safety measures on your website
Creating Trust Through Transparency
Build lasting patient confidence by:
- Openly discussing your sterilization practices
- Responding to safety concerns with empathy and clarity
- Demonstrating sterilization procedures when appropriate
- Maintaining open dialogue about infection control measures
This comprehensive approach to education ensures both staff and patients understand and appreciate your practice's dedication to safety and cleanliness. Through consistent communication and training, you create an environment where sterilization protocols become second nature to your team while reassuring patients of your commitment to their well-being.
Staying Current with Sterilization Techniques and Legal Considerations
Continuing education is vital for staying ahead in the field of dental instrument processing and compliance best practices. Attending workshops and webinars keeps your knowledge up-to-date with new research, best practices and equipment. Staying informed helps ensure the highest standards of care in your dental practice.
Legal and ethical considerations are central to dental instrument sterilization. Adhering to regulations safeguards your practice against potential liabilities and enhances your reputation. Understanding relevant laws and guidelines protects both patients and the dental team.
Establishing a robust infection control policy demonstrates accountability and professionalism. Consistently reviewing and updating these policies is crucial as new pathogens and technologies emerge. An informed practice not only meets but exceeds compliance requirements, fostering a culture of safety and excellence.
Conclusion: Building a Culture of Safety and Compliance
The sterilization of dental instruments plays a critical role in patient safety and trust. Through careful attention to design, proper equipment selection—such as comprehensive sterilization solutions—and rigorous protocol implementation, your practice can maintain the highest standards of safety while operating efficiently.
By investing in high-quality dental equipment sterilization solutions—including autoclaves, ultrasonic cleaners and cabinetry designed to support a dirty-to-clean workflow—you not only protect patients and practice teammates, but also increase efficiency, reduce stress and reinforce your reputation for excellence.
When clinicians and patients alike can see that your sterilization practices are deliberate, effective and well-integrated, it builds trust—and that trust translates into long-term success for your practice.
Let us help you maximize your instrument processing protocols. Schedule a consultation today.
Lubricare 2 is a registered trademark of Bien-Air SA.

 Dental Practice SafetyOur imaging and sterilization workflow solutions help you create a safe environment for all, while maximizing efficiencies and satisfaction for patients and staff.
Dental Practice SafetyOur imaging and sterilization workflow solutions help you create a safe environment for all, while maximizing efficiencies and satisfaction for patients and staff. Smart ViewReliable uptime begins with visibility into equipment performance. Gain real-time insights and maintenance tracking with Smart View™, all within one centralized, secure portal.
Smart ViewReliable uptime begins with visibility into equipment performance. Gain real-time insights and maintenance tracking with Smart View™, all within one centralized, secure portal.
 Ergonomic DentistryOur equipment is designed to promote proper posture for doctors, assistants and patients alike, while helping to provide the workflow that best suits your practice needs.
Ergonomic DentistryOur equipment is designed to promote proper posture for doctors, assistants and patients alike, while helping to provide the workflow that best suits your practice needs.
 High-Performance DentistryImproving your practice performance requires a skillful combination of technology, workflow and expertise in the dental space that only Midmark can provide.
High-Performance DentistryImproving your practice performance requires a skillful combination of technology, workflow and expertise in the dental space that only Midmark can provide.
 Dental SchoolsWe shine in support for dental schools from our reliable professional solutions to our partnerships with colleges and the communities they serve.
Dental SchoolsWe shine in support for dental schools from our reliable professional solutions to our partnerships with colleges and the communities they serve.
 Dental Support Organizations (DSO)With a broad range of clinical solutions, short product lead times and reliable support, we provide a consistent experience that lets you better serve your patients.
Dental Support Organizations (DSO)With a broad range of clinical solutions, short product lead times and reliable support, we provide a consistent experience that lets you better serve your patients.
 Independent DentistsOur total equipment solutions and clinical design specialists are standing by to help, you can get back to focusing on the exceptional care you provide to your patients.
Independent DentistsOur total equipment solutions and clinical design specialists are standing by to help, you can get back to focusing on the exceptional care you provide to your patients.
 Architectural ResourcesVisit our planning and design library for the architectural resources you need.
Architectural ResourcesVisit our planning and design library for the architectural resources you need. ImpactDesignAttend this workshop to learn how to define, refine and achieve your practice goals through effective dental office design principles.
ImpactDesignAttend this workshop to learn how to define, refine and achieve your practice goals through effective dental office design principles. Multi-Site MasteryMulti-Site Mastery is an immersive learning experience designed for dental leaders ready to take their organization to the next level.
Multi-Site MasteryMulti-Site Mastery is an immersive learning experience designed for dental leaders ready to take their organization to the next level.
 The Midmark ExperienceStart Here to Make Your Dream Office a Reality
The Midmark ExperienceStart Here to Make Your Dream Office a Reality

 Midmark Choice PLUS PromotionPair any Midmark dental chair with a Procenter doctor’s delivery system to receive 20% off your chair, delivery system and other eligible options—plus a free Midmark LED operatory light.
Midmark Choice PLUS PromotionPair any Midmark dental chair with a Procenter doctor’s delivery system to receive 20% off your chair, delivery system and other eligible options—plus a free Midmark LED operatory light. Midmark Choice PackagePair a Midmark Ultra-series dental chair and Asepsis 21® doctor's delivery system to receive 20% off your chair, delivery system and additional eligible options.
Midmark Choice PackagePair a Midmark Ultra-series dental chair and Asepsis 21® doctor's delivery system to receive 20% off your chair, delivery system and additional eligible options. Mechanical Room PromotionUpgrade to Midmark air compressor and vacuum equipment now to claim free accessories and special savings.
Mechanical Room PromotionUpgrade to Midmark air compressor and vacuum equipment now to claim free accessories and special savings. Midmark Preva Intraoral X-Ray PromotionThe order period has ended, but you can still claim your incentives through March 31, 2026. Redeem here.
Midmark Preva Intraoral X-Ray PromotionThe order period has ended, but you can still claim your incentives through March 31, 2026. Redeem here. Product LiteratureDesigning the best healthcare experience isn’t always easy. We can help.
Product LiteratureDesigning the best healthcare experience isn’t always easy. We can help.
 Product SpecificationsReview features and technical specifications for the products you want to learn more about.
Product SpecificationsReview features and technical specifications for the products you want to learn more about. InfographicsSee the whole picture with visual explanations and real-world applications.
InfographicsSee the whole picture with visual explanations and real-world applications. Webinars + PodcastsView and listen to the latest from Midmark here
Webinars + PodcastsView and listen to the latest from Midmark here EbooksLearn what we’ve uncovered about designing better care.
EbooksLearn what we’ve uncovered about designing better care. ImpactDesignAttend this workshop to learn how to define, refine and achieve your practice goals through effective dental office design principles.
ImpactDesignAttend this workshop to learn how to define, refine and achieve your practice goals through effective dental office design principles. Multi-Site MasteryMulti-Site Mastery is an immersive learning experience designed for dental leaders ready to take their organization to the next level.
Multi-Site MasteryMulti-Site Mastery is an immersive learning experience designed for dental leaders ready to take their organization to the next level.
 Service + Support | DentalAsk our Customer Experience team for help with product information, promotion details or contacting a sales representative.
Service + Support | DentalAsk our Customer Experience team for help with product information, promotion details or contacting a sales representative.
 Product Manuals (Technical Library)Discover everything you need to know about our products in one location.
Product Manuals (Technical Library)Discover everything you need to know about our products in one location.
 Technical Support | DentalFind parts, documentation and more with the help of our dedicated Technical Service representatives.
Technical Support | DentalFind parts, documentation and more with the help of our dedicated Technical Service representatives. Delivery + Installation ServicesMidmark Delivery Services will professionally manage your Midmark equipment shipping, delivery, staging and installation for maximum project success.
Delivery + Installation ServicesMidmark Delivery Services will professionally manage your Midmark equipment shipping, delivery, staging and installation for maximum project success.