Industries
-
 Veterinary MedicineOur innovative solutions are designed and manufactured to withstand the demands of veterinary medicine and provide the highest quality of care.
Veterinary MedicineOur innovative solutions are designed and manufactured to withstand the demands of veterinary medicine and provide the highest quality of care. -
 BoardingMidmark offers durable housing solutions that help prevent cross-contamination and provide ample space for an exceptional patient experience.
BoardingMidmark offers durable housing solutions that help prevent cross-contamination and provide ample space for an exceptional patient experience. -
 Shelters + Animal WelfareComfortable housing for companion animals that helps reduce stress and allows personalities to shine--increasing chances of finding forever homes.
Shelters + Animal WelfareComfortable housing for companion animals that helps reduce stress and allows personalities to shine--increasing chances of finding forever homes.
-

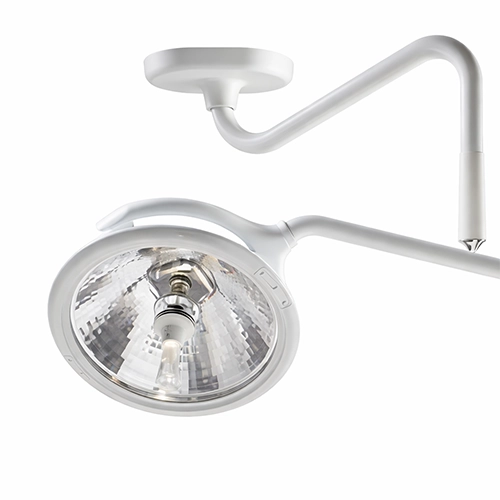
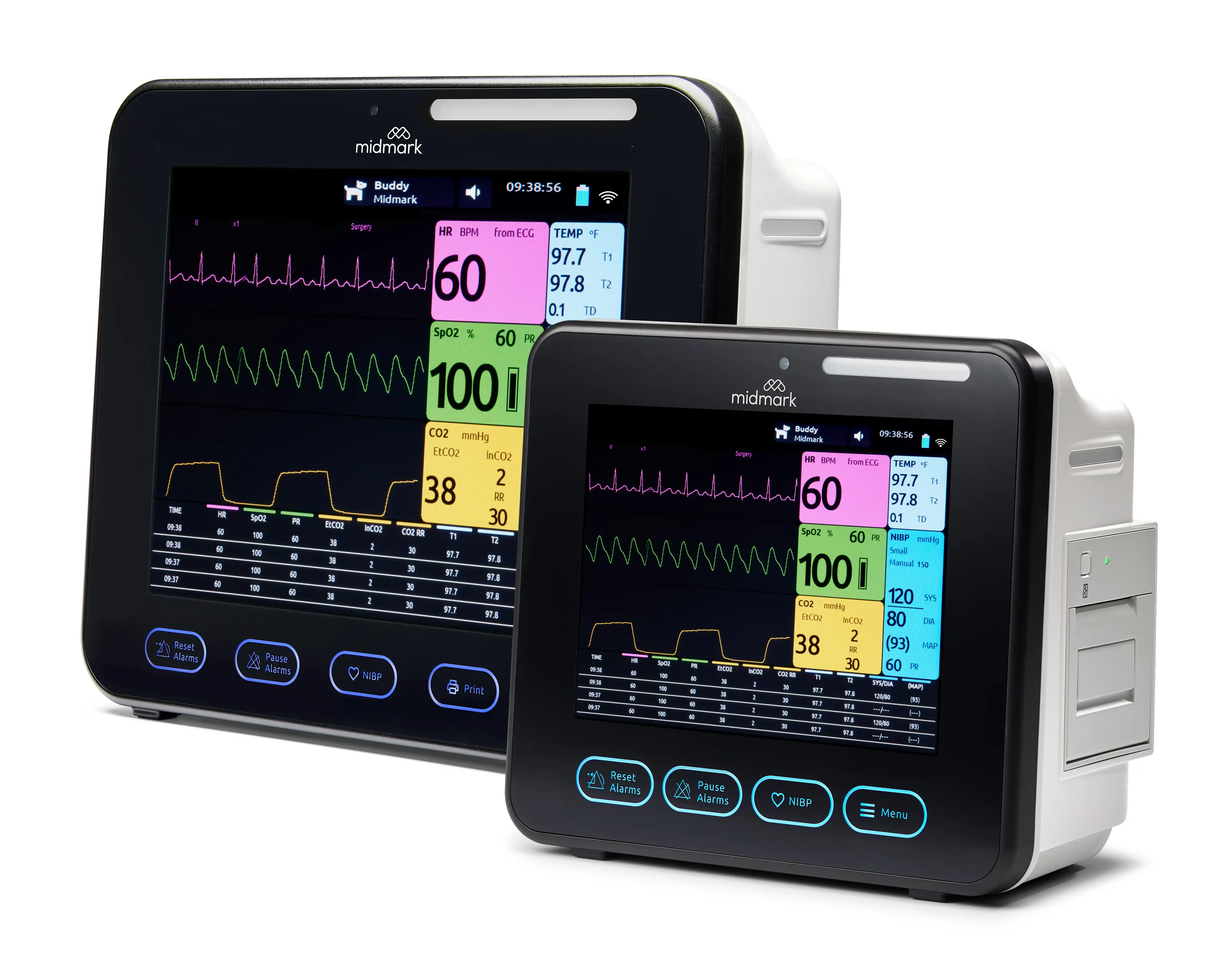
 Anesthesia + MonitoringBrowse our industry-leading solutions and let us help you provide a better experience for all patients and providers
Anesthesia + MonitoringBrowse our industry-leading solutions and let us help you provide a better experience for all patients and providers -

 Comprehensive Dentistry SolutionsAdding dental services to your animal health practice promotes overall patient health—and it’s good for business.
Comprehensive Dentistry SolutionsAdding dental services to your animal health practice promotes overall patient health—and it’s good for business. -
 Animal HousingFrom kennels and modular cage units to stylish condos and suites, create a warm and welcoming environment without sacrificing aesthetics or functionality.
Animal HousingFrom kennels and modular cage units to stylish condos and suites, create a warm and welcoming environment without sacrificing aesthetics or functionality.
-
 Architectural ResourcesVisit our planning and design library for the REVIT files, CAD drawings and LEED credit summaries you need for your project.
Architectural ResourcesVisit our planning and design library for the REVIT files, CAD drawings and LEED credit summaries you need for your project. -
 Cage Bank ConfiguratorExplore the options in our configurator to create the best solution for your clinic.
Cage Bank ConfiguratorExplore the options in our configurator to create the best solution for your clinic. -
 Delivery + Installation ServicesMidmark Delivery Services will professionally manage your Midmark equipment shipping, delivery, staging and installation for maximum project success.
Delivery + Installation ServicesMidmark Delivery Services will professionally manage your Midmark equipment shipping, delivery, staging and installation for maximum project success.

Building your dream clinic can be both exciting and scary.
But you don’t have to do it alone. Let us help you design
a space perfectly suited to you and your team.
-
 BlogLet’s talk about better care. Join the discussion today.
BlogLet’s talk about better care. Join the discussion today. -
 Product CatalogsDesigning the best animal care experience isn’t always easy. We can help.
Product CatalogsDesigning the best animal care experience isn’t always easy. We can help. -
 Product LiteratureSee how we’re helping our customers design better, more efficient care.
Product LiteratureSee how we’re helping our customers design better, more efficient care. -
 VideosWe’re committed to innovation and are grounded in learning – see what we’ve uncovered.
VideosWe’re committed to innovation and are grounded in learning – see what we’ve uncovered.
-
 Delivery + Installation ServicesMidmark Delivery Services will professionally manage your Midmark equipment shipping, delivery, staging and installation for maximum project success.
Delivery + Installation ServicesMidmark Delivery Services will professionally manage your Midmark equipment shipping, delivery, staging and installation for maximum project success. -
 Product Repair + Service SolutionsExpert technical support, parts, onsite repairs and extended warranties for your Midmark medical equipment. Services you can trust.
Product Repair + Service SolutionsExpert technical support, parts, onsite repairs and extended warranties for your Midmark medical equipment. Services you can trust.
-
 Product Manuals (Technical Library)
Product Manuals (Technical Library) -

 Shop Parts, Software + ServicesVisit The Online Parts Store for 24/7 ordering.
Shop Parts, Software + ServicesVisit The Online Parts Store for 24/7 ordering. -
 Animal Health Technical SupportLet our dedicated technical service team help you find parts, documentation and more.
Animal Health Technical SupportLet our dedicated technical service team help you find parts, documentation and more. -

 Customer ExperienceOur friendly support team is here to assist you every step of the way.
Customer ExperienceOur friendly support team is here to assist you every step of the way.